Hair Follicle Growth Cycle & Minoxidil
To better understand the benefits of Minoxodil,
it’s helpful to first consider the hair follicle growth cycle.
HAIR FOLLICLE GROWTH CYCLE
Hair follicles normally exist in three phases:
1. A growth period called the Anagen phase, typically lasting around three years, followed by
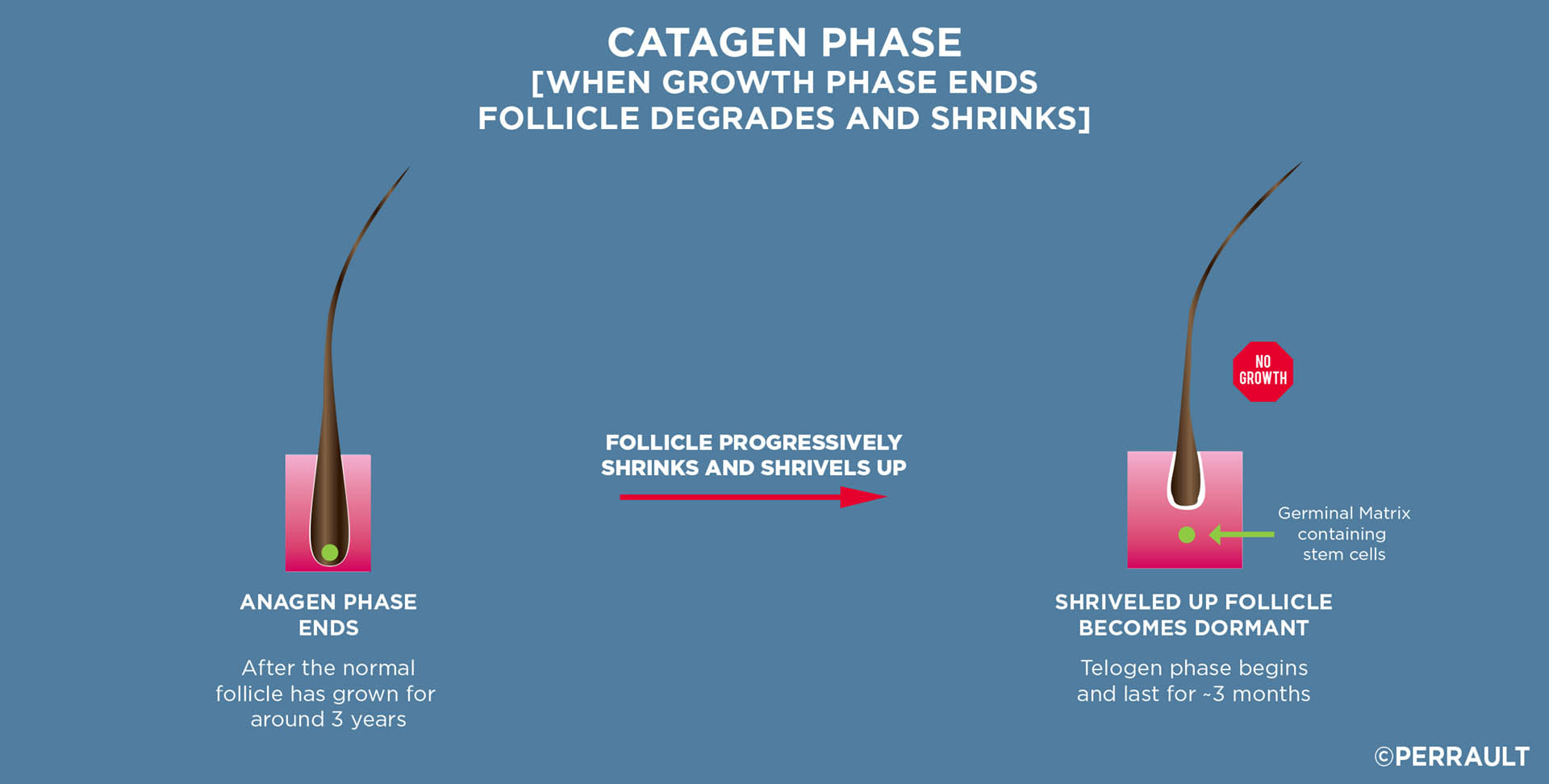
2. A brief shriveling up period called the Catagen phase, followed by
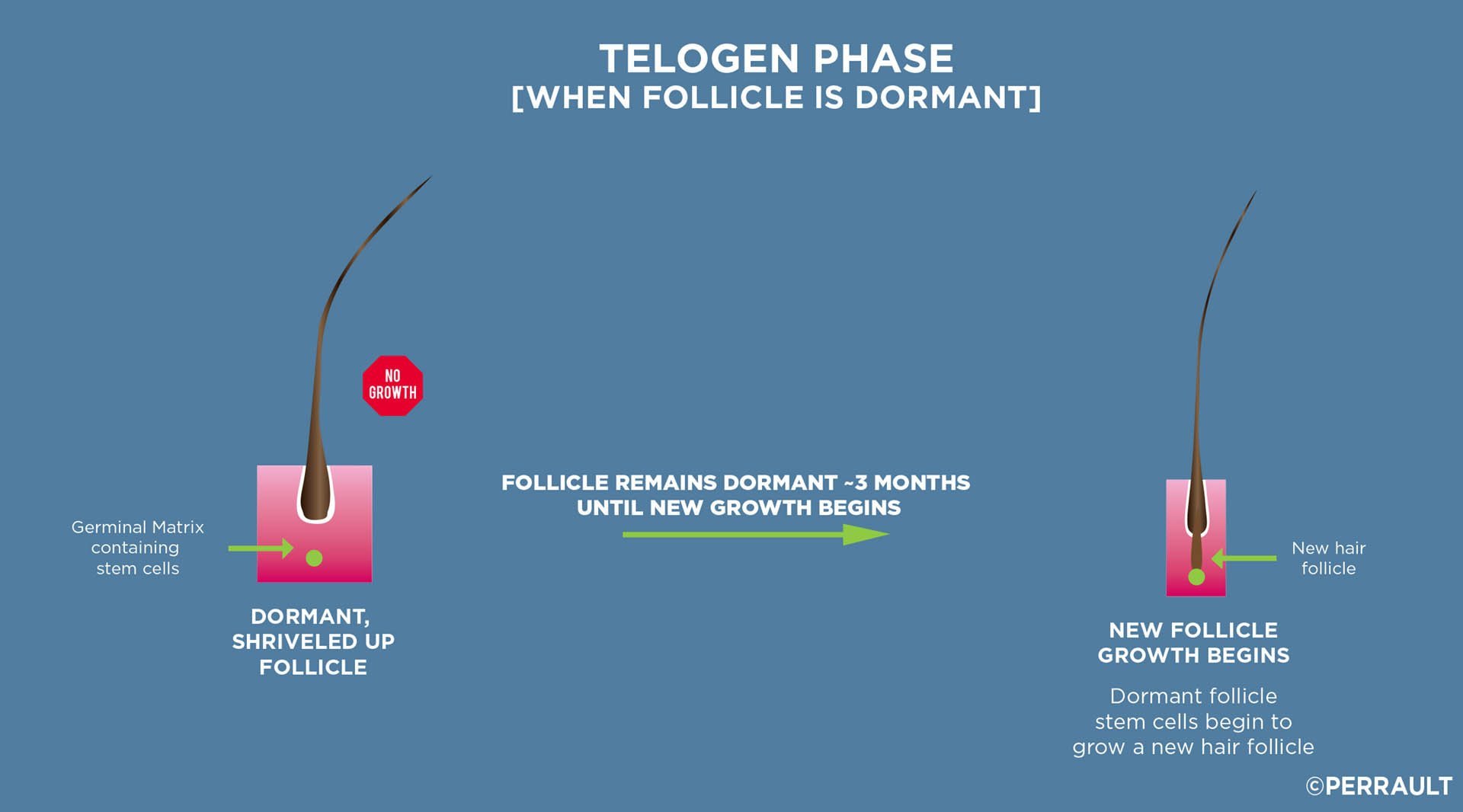
3. A dormant or resting period called the Telogen phase, usually lasting three months.
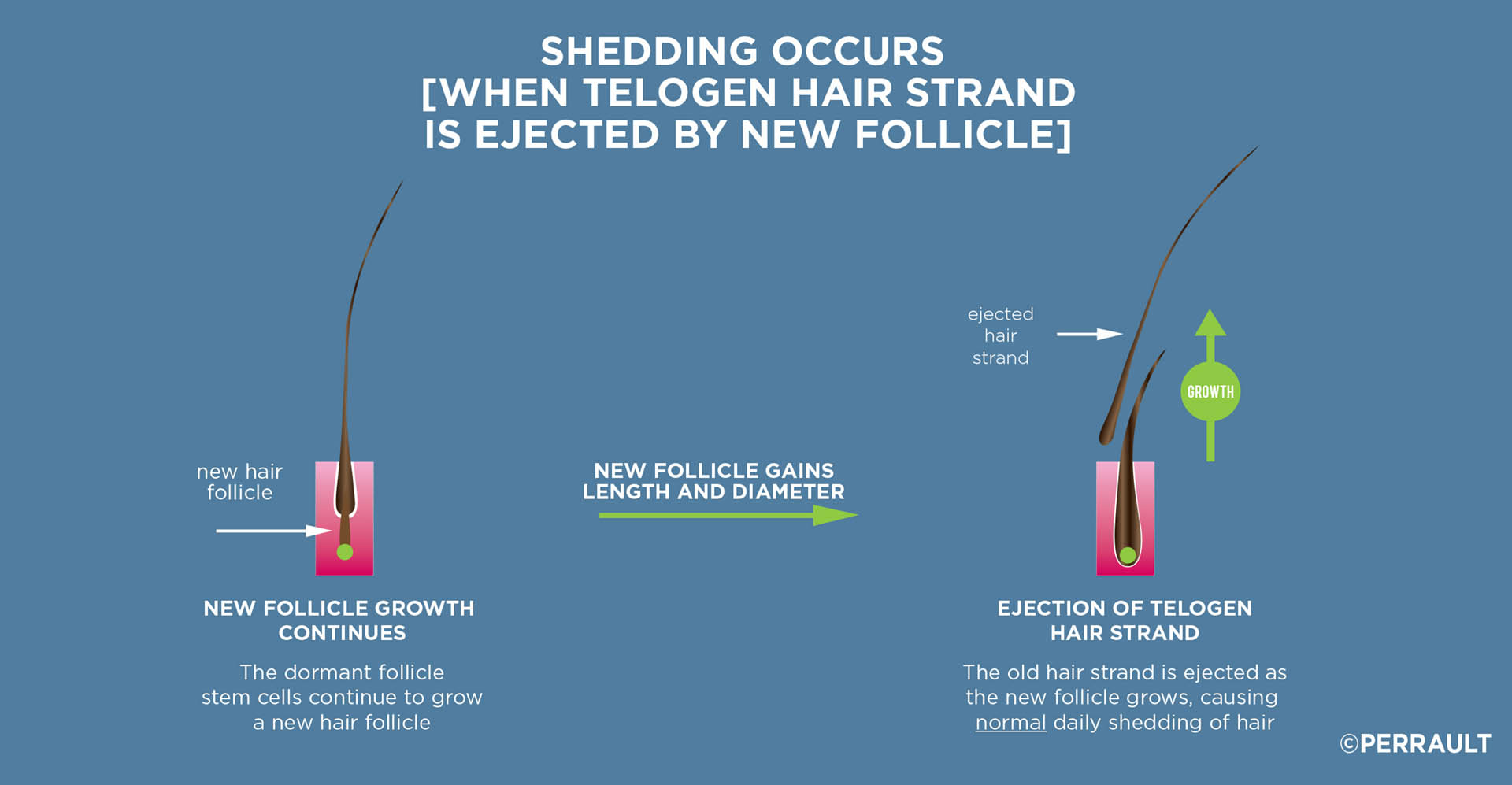
A normal hair follicle will typically grow for three years, shrivel up and become domant for three months, before regrowing a new strand of hair. As the new hair grows and lengthens, it ejects the old hair strand resulting in the normal shedding of hair that we experience every day.
We normally shed up to 50 or more hairs per day. This cycling will typically allow the hair strand to grow about 18 inches (i.e. shoulder length hair) before it sheds. Some exceptional individuals have a longer growth cycle and can achieve greater hair length.
Normally, 90% of our follicles are in the growth phase, growing approximately one half inch per month.

.
.
.
.

REVERSING HAIR LOSS
“Effluvium” is the medical term for hair shedding. Telogen Effluvium is the shedding that occurs as a result of the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. Normally around 10% of our hair follicles are in a resting or telogen state. Daily shedding occurs when resting follicles begin to grow and eject dormant hair follicles.
Abnormal Telogen Effluvium occurs when large numbers of hair follicles prematurely enter into the
Telogen phase (or resting phase); abnormal/excessive shedding occurs around three months following a physiologic change or trigger (i.e. medication change, fad diets, severe weight loss, after childbirth, etc.)
In some patients, their follicles are hypersensitive to numerous triggers, causing constant Telogen Effluvium episodes. This condition, referred to as Chronic Telogen Effluvium, may be improved with lifestyle changes and medication.
MINOXIDIL (TOPICAL & LOW-DOSE ORAL)
Minoxidil is a medication that dilates blood vessels, originally developed in the late 1950s by Upjohn Company. Minoxidil was first approved by the FDA in 1979 for treatment of high blood pressure, in the form of an oral tablet. Studies conducted for Minoxidil as an anti-hypertensive medication showed unexpected hair growth and led to its development as a treatment for hair loss. The over-the-counter product Rogaine for men, contains 5% Minoxidil. Rogaine for women initially
contained 2% Minoxidil, but is now 5% as well.
In contrast to Finasteride and Dutasteride, Minoxidil does not affect DHT. Minoxidil appears to
improve hair loss by increasing the Anagen phase, or growth phase period, of the hair growth cycle. This allows the miniaturized follicles to grow longer and gain greater diameter. The longer, thicker hairs have more volume and provide better coverage.
LOW-DOSE ORAL MINOXIDIL
In recent years, Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil has gained popularity as a more convenient alternative to Topical Minoxidil. Typically, a 2.5 mg oral Minoxidil tablet is divided in half, and one-half tablet (1.25 mg) is taken daily. A recent study found that “Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil has a good safety profile when used as a treatment for hair loss.”
Oral and Topical Minoxidil have also been found to be helpful in treating patients with hair loss from acute and chronic forms of Telogen Effluvium as well as many other forms of hair loss.